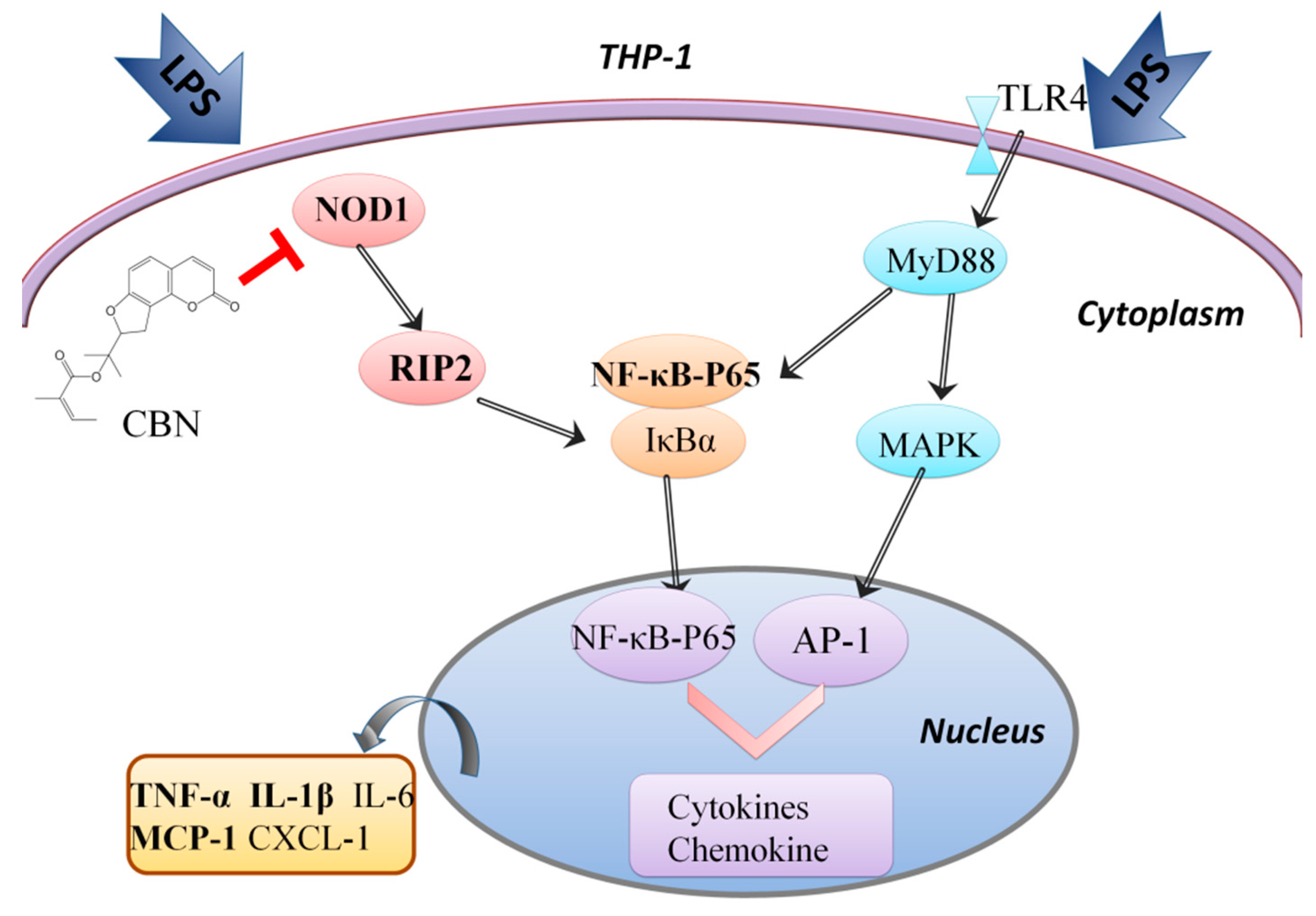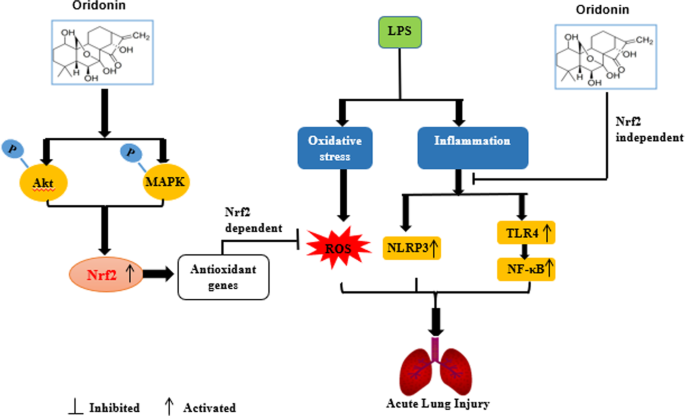
Oridonin protects LPS-induced acute lung injury by modulating Nrf2-mediated oxidative stress and Nrf2-independent NLRP3 and NF-κB pathways | Cell Communication and Signaling | Full Text
The Anti-Inflammatory Effects and Mechanisms of Eupafolin in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Responses in RAW264.7 Macrophages

2′-Hydroxy-5′-methoxyacetophenone attenuates the inflammatory response in LPS-induced BV-2 and RAW264.7 cells via NF-κB signaling pathway - ScienceDirect
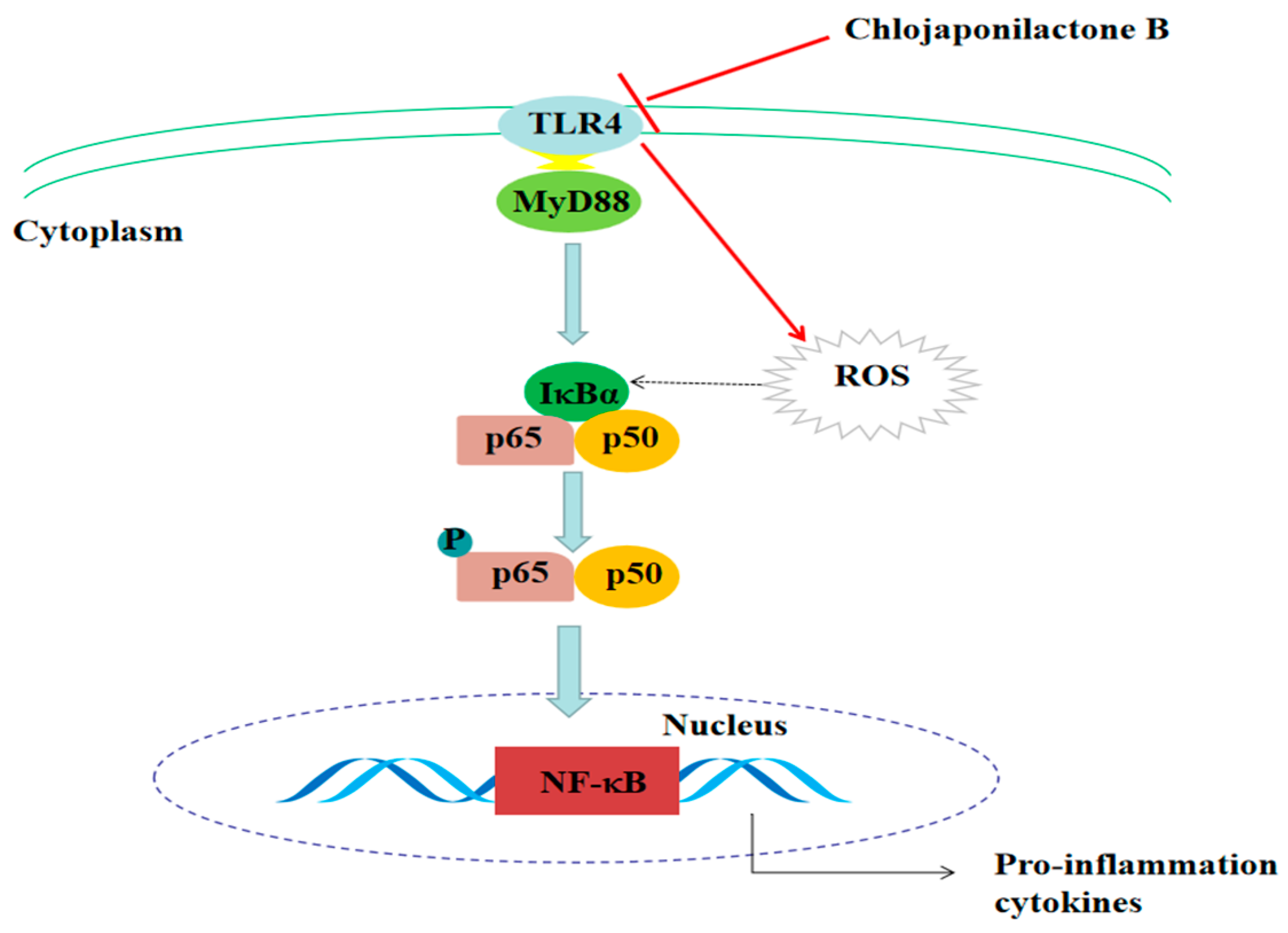
Molecules | Free Full-Text | Chlojaponilactone B Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Responses by Suppressing TLR4-Mediated ROS Generation and NF-κB Signaling Pathway | HTML

Eriocitrin in combination with resveratrol ameliorates LPS-induced inflammation in RAW264.7 cells and relieves TPA-induced mouse ear edema - ScienceDirect
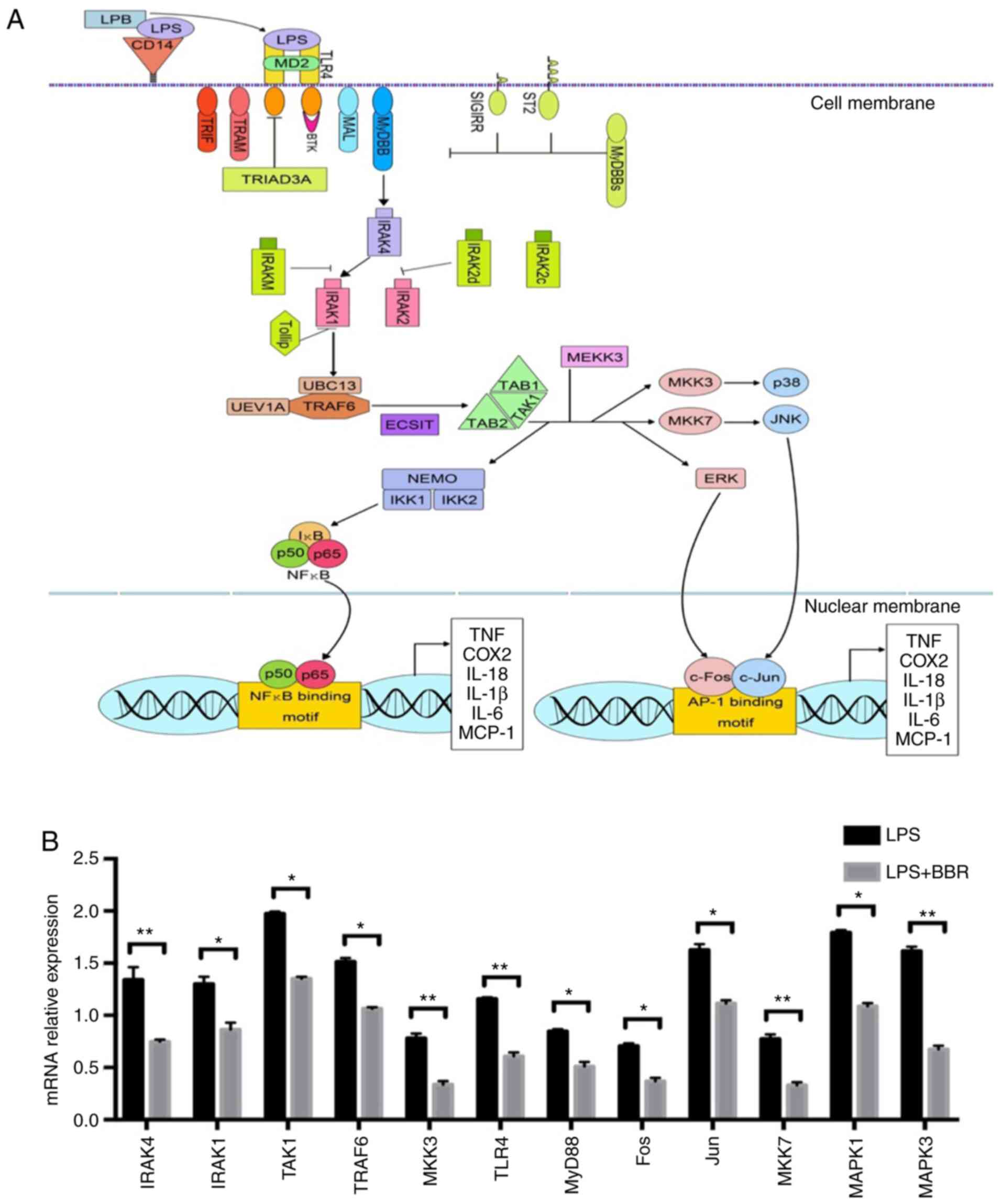
Anti‑inflammatory mechanism of berberine on lipopolysaccharide‑induced IEC‑18 models based on comparative transcriptomics
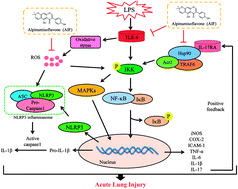
Alpinumisoflavone attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by regulating the effects of anti-oxidation and anti-inflammation both in vitro and in vivo - RSC Advances (RSC Publishing)
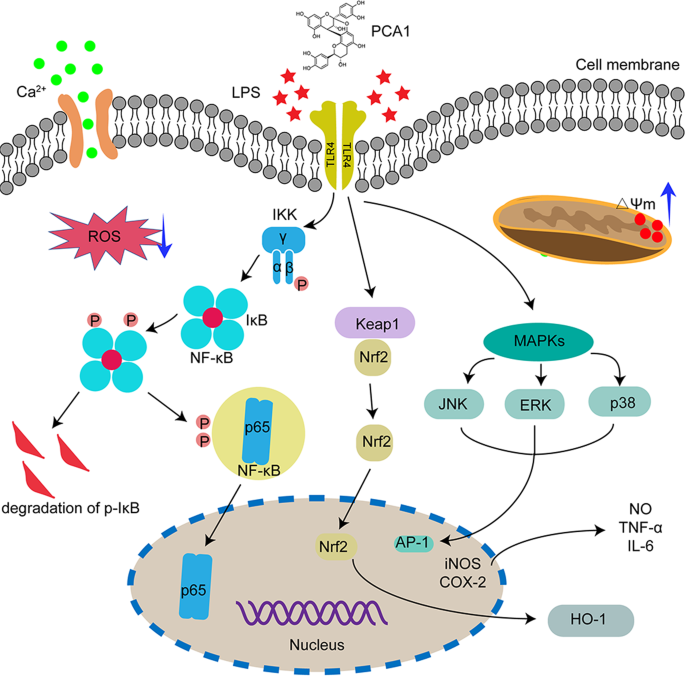
Procyanidin A1 Alleviates Inflammatory Response induced by LPS through NF-κB, MAPK, and Nrf2/HO-1 Pathways in RAW264.7 cells | Scientific Reports
PLOS ONE: 4'-Hydroxywogonin suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses in RAW 264.7 macrophages and acute lung injury mice
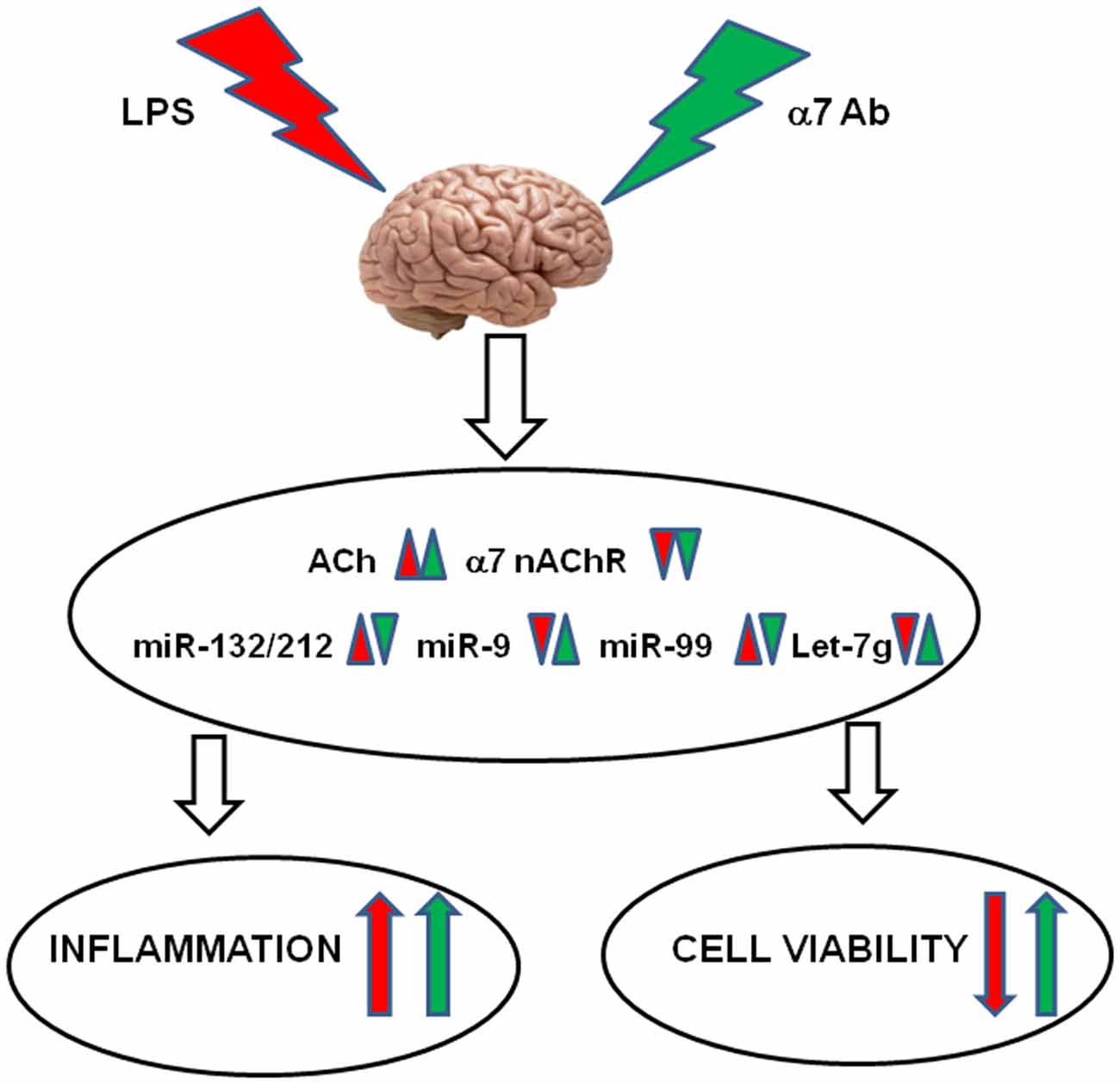
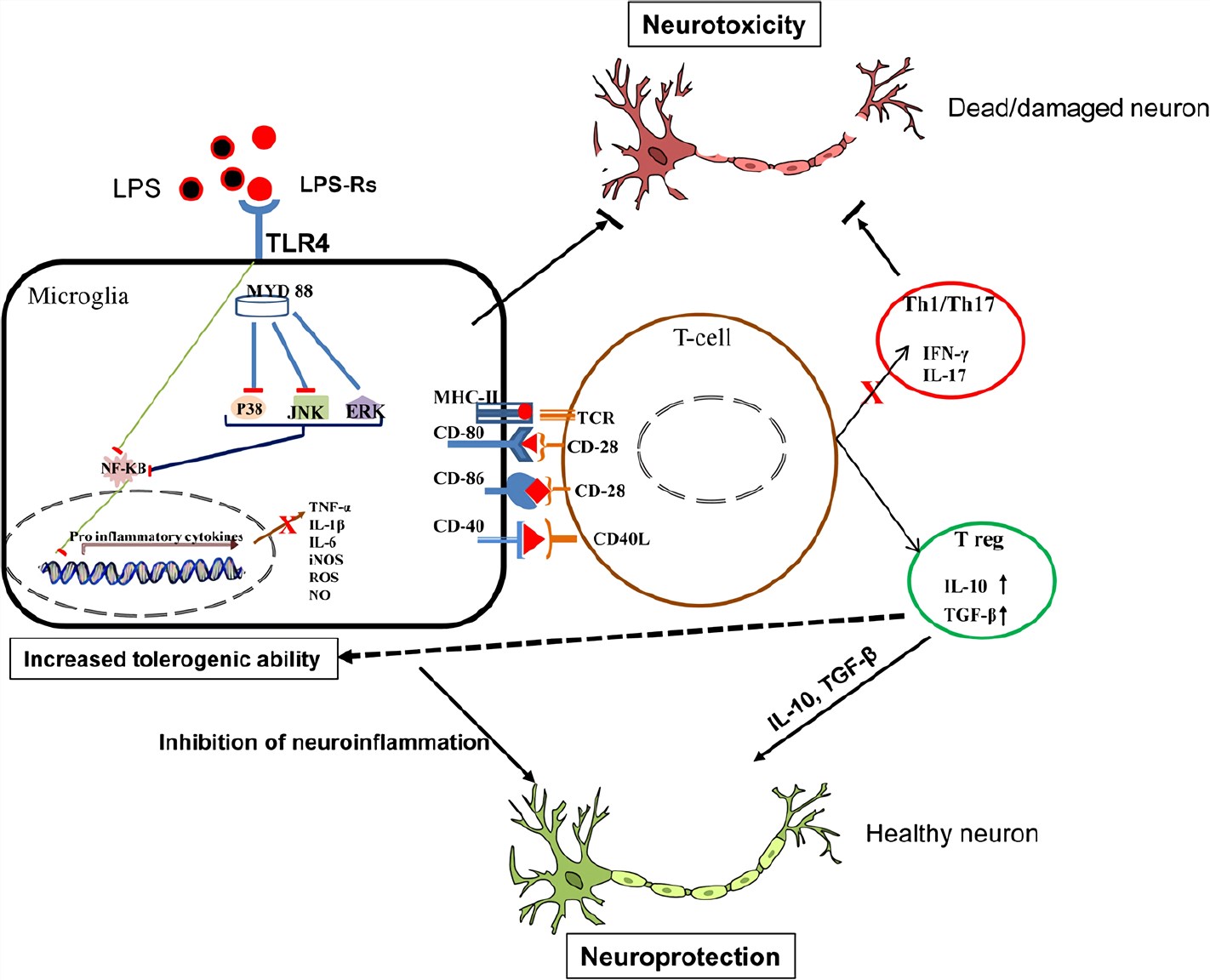
Frontiers | Molecular Mechanisms Regulating LPS-Induced Inflammation in the Brain | Molecular Neuroscience
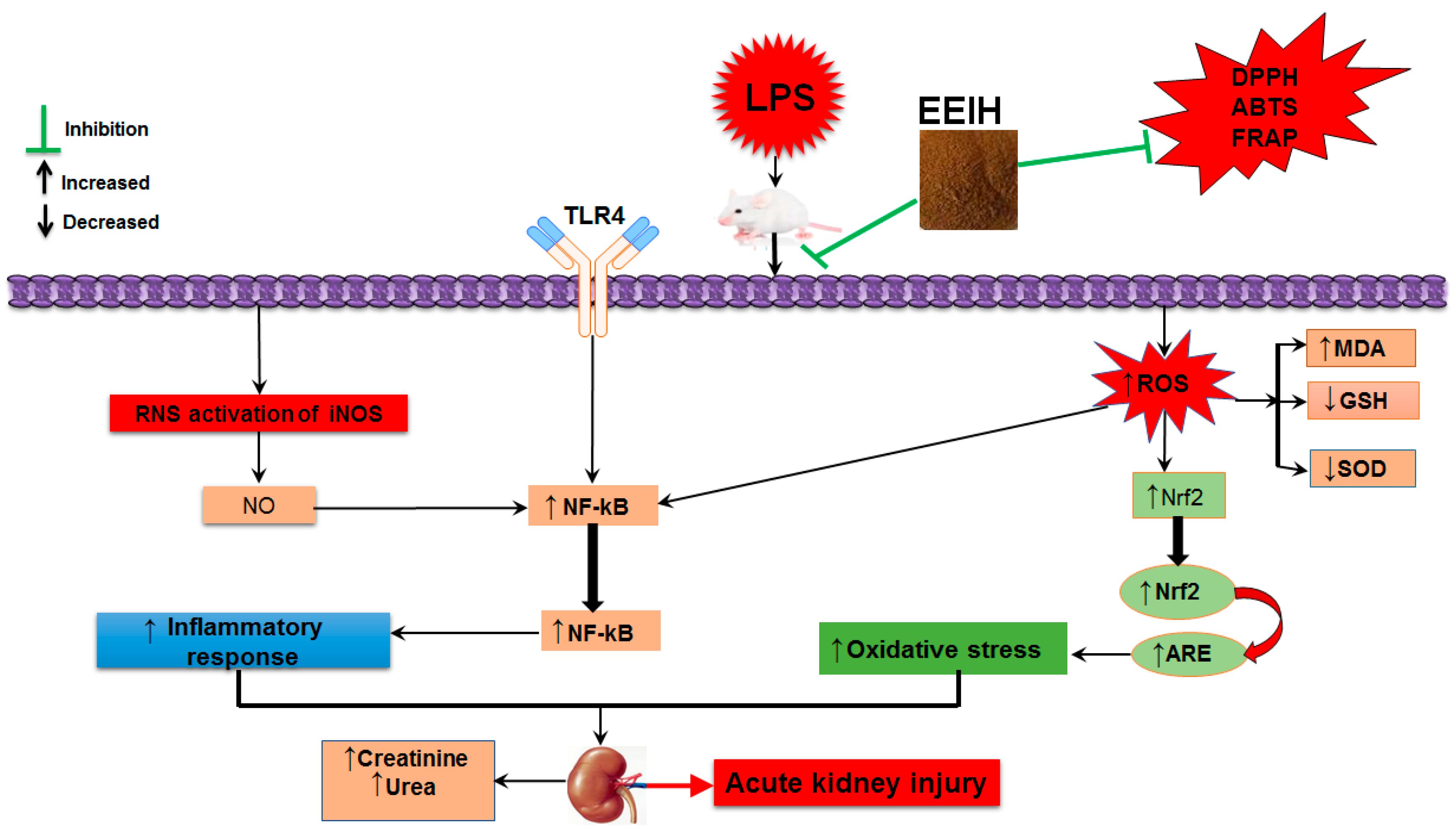
Nutrients | Free Full-Text | Ethanol Extract of Illicium henryi Attenuates LPS-Induced Acute Kidney Injury in Mice via Regulating Inflammation and Oxidative Stress | HTML
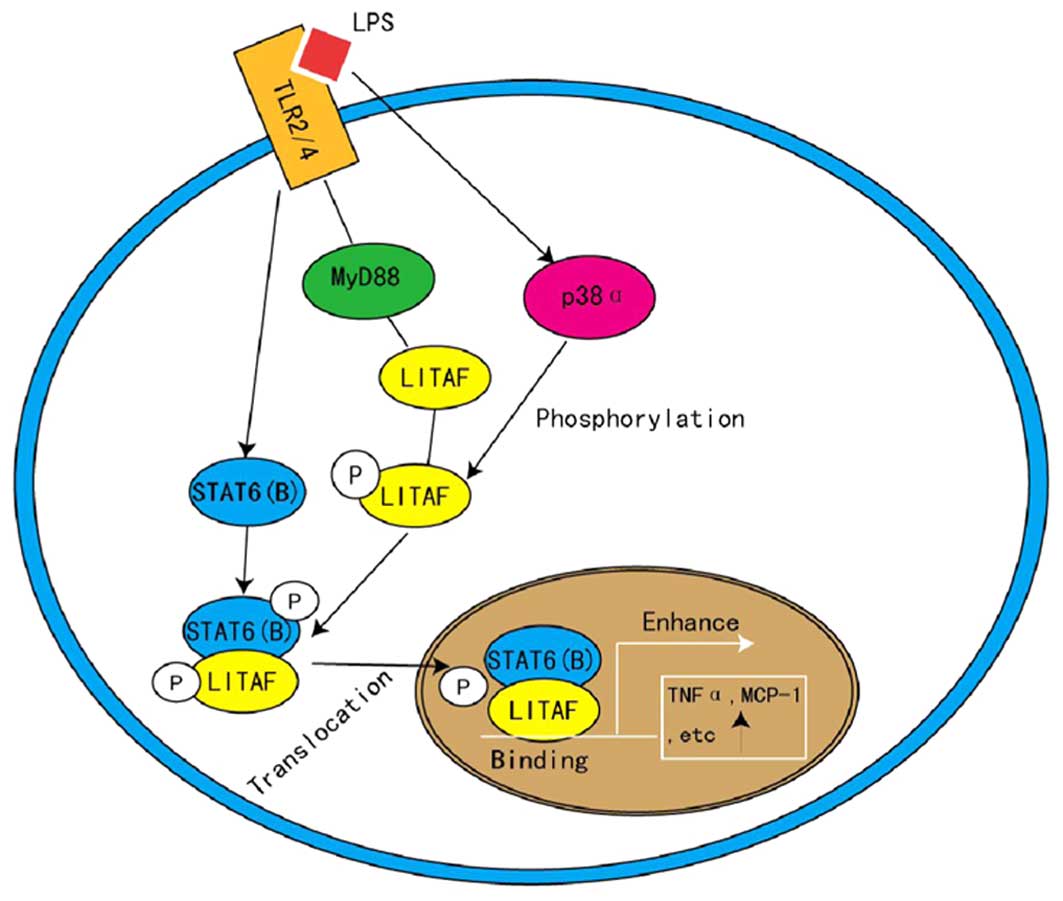
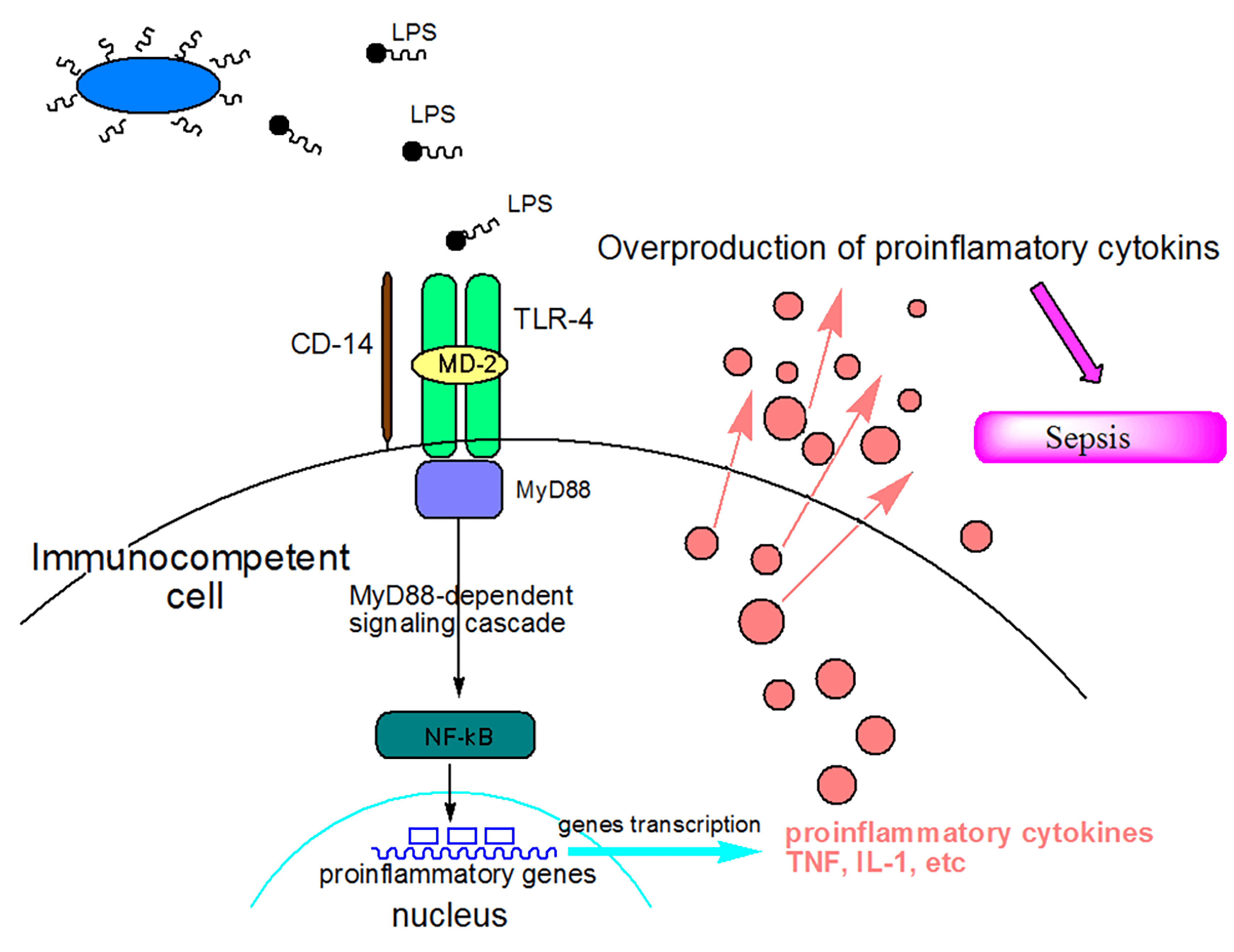
Lipopolysaccharide-induced tumor necrosis factor-α factor enhances inflammation and is associated with cancer (Review)
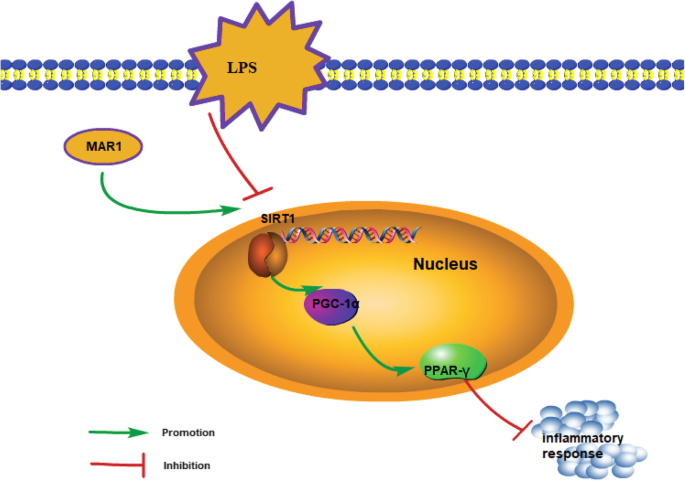
MAR1 suppresses inflammatory response in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 macrophages and human primary peripheral blood mononuclear cells via the SIRT1/PGC-1α/PPAR-γ pathway | Journal of Inflammation | Full Text

Inhibitory Effect of Jing-Fang Powder n-Butanol Extract and Its Isolated Fraction D on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation in RAW264.7 Cells | Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics
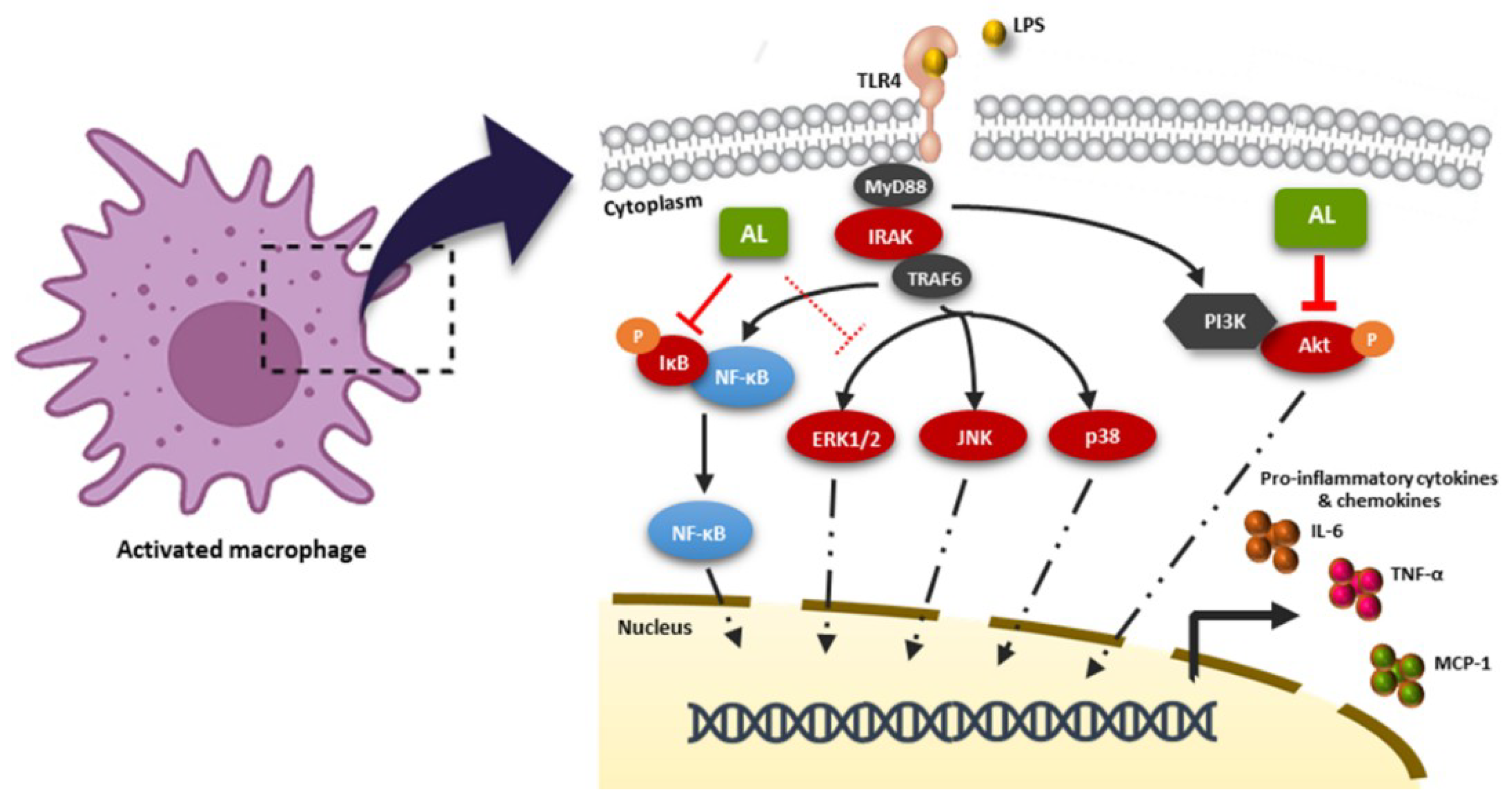
IJMS | Free Full-Text | Artocarpus lakoocha Extract Inhibits LPS-Induced Inflammatory Response in RAW 264.7 Macrophage Cells

Activation of CB1R Promotes Lipopolysaccharide-Induced IL-10 Secretion by Monocytic Myeloid-Derived Suppressive Cells and Reduces Acute Inflammation and Organ Injury | The Journal of Immunology

Directly interact with Keap1 and LPS is involved in the anti-inflammatory mechanisms of (-)-epicatechin-3-gallate in LPS-induced macrophages and endotoxemia - ScienceDirect